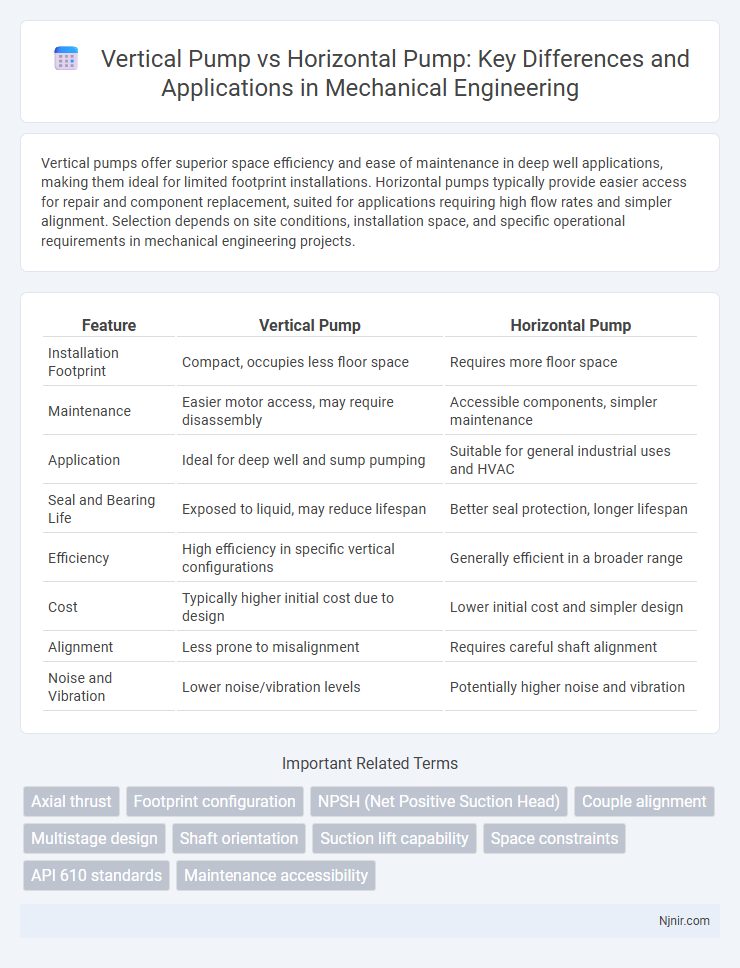
Vertical pumps offer superior space efficiency and ease of maintenance in deep well applications, making them ideal for limited footprint installations. Horizontal pumps typically provide easier access for repair and component replacement, suited for applications requiring high flow rates and simpler alignment. Selection depends on site conditions, installation space, and specific operational requirements in mechanical engineering projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vertical Pump | Horizontal Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Footprint | Compact, occupies less floor space | Requires more floor space |
| Maintenance | Easier motor access, may require disassembly | Accessible components, simpler maintenance |
| Application | Ideal for deep well and sump pumping | Suitable for general industrial uses and HVAC |
| Seal and Bearing Life | Exposed to liquid, may reduce lifespan | Better seal protection, longer lifespan |
| Efficiency | High efficiency in specific vertical configurations | Generally efficient in a broader range |
| Cost | Typically higher initial cost due to design | Lower initial cost and simpler design |
| Alignment | Less prone to misalignment | Requires careful shaft alignment |
| Noise and Vibration | Lower noise/vibration levels | Potentially higher noise and vibration |
Overview of Vertical and Horizontal Pumps
Vertical pumps are designed with a vertical shaft orientation, making them ideal for deep well and sump applications where space is limited. Horizontal pumps have a shaft that lies parallel to the ground, providing easier maintenance and installation in industrial settings with ample floor space. Both pump types are used for fluid transfer, but selection depends on factors such as space availability, ease of access, and specific application requirements.
Key Differences in Design
Vertical pumps feature an upright shaft configuration with the motor mounted above the pump, making them ideal for deep sump or well applications, while horizontal pumps have a shaft positioned horizontally with a motor aligned beside the pump casing for easier maintenance. Vertical pump designs often incorporate a multi-stage impeller set for high-pressure delivery, whereas horizontal pumps typically use single or multi-stage impellers suited for moderate pressure and flow rates. The compact footprint of vertical pumps contrasts with the more accessible layout of horizontal pumps, influencing installation space and operational environment suitability.
Applications: Where Each Pump Excels
Vertical pumps excel in applications requiring deep well extraction, such as groundwater and sewage treatment, due to their space-saving design and ability to handle large volumes at high pressures. Horizontal pumps are preferred in industrial processes and HVAC systems where easier maintenance, installation flexibility, and handling of viscous fluids are critical. Both designs optimize performance based on specific operational needs like flow rate, head, and environmental constraints.
Installation Requirements and Space Considerations
Vertical pumps require minimal floor space due to their upright orientation, making them ideal for installations with limited room or confined areas. Horizontal pumps demand more horizontal clearance and often need additional foundation support, which can increase installation complexity and space usage. Proper alignment and access for maintenance are crucial for both, but vertical pumps typically allow easier access in tight spaces.
Maintenance and Accessibility
Vertical pumps feature a compact design that simplifies maintenance by allowing easy access to the motor and pump components without requiring disassembly of the entire unit, reducing downtime and labor costs. Horizontal pumps provide straightforward accessibility to mechanical seals and bearings, facilitating routine inspections and repairs, which can be advantageous in environments where floor space is abundant. Selection between the two often depends on site constraints and maintenance preferences, with vertical pumps favored in tight spaces and horizontal pumps chosen for ease of component replacement.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Vertical pumps typically offer higher efficiency in applications requiring deep suction lifts due to their direct coupling to a submerged impeller, reducing energy losses and improving hydraulic performance. Horizontal pumps, while easier to maintain and install, may experience lower efficiency at high flow rates because of increased shaft length and bearing friction. Efficiency comparison shows vertical pumps excel in deep well or sump scenarios, whereas horizontal pumps perform better in low to moderate head applications with easier access for routine maintenance.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term
Vertical pumps generally have a lower initial installation cost due to their compact footprint and reduced civil work requirements compared to horizontal pumps. However, horizontal pumps often offer easier maintenance access, potentially lowering long-term operational and repair expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing upfront capital expenditures with anticipated maintenance, energy efficiency, and lifespan differences between vertical and horizontal pump designs.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Vertical pumps often face common issues like shaft misalignment, bearing failure, and seal leaks due to their design and installation constraints. Horizontal pumps typically encounter problems such as coupling misalignment, impeller damage, and casing wear, which affect performance and efficiency. Troubleshooting both types requires regular inspection of seals, bearings, and alignment, alongside vibration analysis to detect early signs of mechanical failure.
Material Compatibility and Durability
Vertical pumps are often preferred in applications requiring high material compatibility and durability due to their design, which minimizes exposure to corrosive substances and abrasive particles. Horizontal pumps, while easier to maintain, may suffer from increased wear and corrosion because their components are more directly exposed to the pumped fluid. Materials like stainless steel, duplex alloys, and specialized coatings enhance the durability of both pump types, but vertical configurations typically offer superior longevity in aggressive chemical environments.
Choosing the Right Pump for Your Project
Selecting the right pump for your project depends on factors such as installation space, maintenance access, and flow requirements. Vertical pumps offer a smaller footprint and are ideal for deep well or sump applications, while horizontal pumps provide easier accessibility for service and are suited for applications with limited vertical clearance. Evaluating site conditions and operational needs ensures optimal pump performance and longevity.
Axial thrust
Vertical pumps generally handle axial thrust more effectively due to their design that directs thrust along the pump shaft into the thrust bearing, whereas horizontal pumps require separate thrust bearings to manage axial loads.
Footprint configuration
Vertical pumps have a smaller footprint configuration compared to horizontal pumps, making them ideal for limited floor space installations.
NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head)
Vertical pumps generally require lower NPSH compared to horizontal pumps due to their inlet design minimizing suction lift and reducing cavitation risk.
Couple alignment
Vertical pumps typically feature simpler couple alignment due to their upright shaft design, whereas horizontal pumps require precise couple alignment to prevent shaft misalignment and ensure optimal performance.
Multistage design
Multistage vertical pumps offer superior space efficiency and higher pressure capabilities compared to horizontal pumps, making them ideal for deep well applications and high-pressure fluid transfer.
Shaft orientation
Vertical pumps feature a shaft oriented vertically, enabling compact installation and efficient handling of deep suction applications, while horizontal pumps have a horizontally aligned shaft that allows easier maintenance and installation in shallow or accessible spaces.
Suction lift capability
Vertical pumps typically offer superior suction lift capability compared to horizontal pumps due to their design that minimizes priming issues and maintains better vapor pressure conditions.
Space constraints
Vertical pumps require less floor space compared to horizontal pumps, making them ideal for installations with significant space constraints.
API 610 standards
API 610 standards specify that vertical pumps are preferred for deep well and sump applications due to their shaft alignment benefits and ease of sealing, while horizontal pumps are favored for ease of maintenance and lower installation height in API-compliant process industries.
Maintenance accessibility
Vertical pumps offer superior maintenance accessibility by allowing easier access to internal components without extensive disassembly compared to horizontal pumps.
vertical pump vs horizontal pump Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com